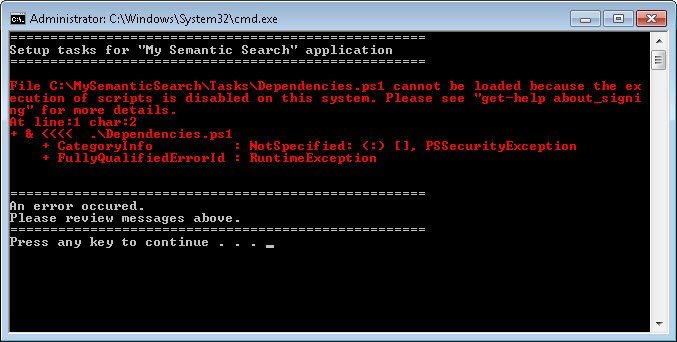
Yesterday I formatted my computer and did a fresh install as it was due from a long time. After the fresh install when I tried to install Semantic Search application using PowerShell, I was stopped by the following error. The error was related to an execution of scripts.
SQL SERVER – DVM sys.dm_os_sys_info Column Name Changed in SQL Server 2012
SQL SERVER – DVM sys.dm_os_sys_info Column Name Changed in SQL Server. Let us learn about it in today’s blog post.
SQL SERVER – 2012 – Summary of All the Analytic Functions – MSDN and SQLAuthority
SQL Server 2012 (RC0 Available here) has introduced new analytic functions. These functions were long awaited and I am glad that they are now here. Before when any of this function was needed, people used to write long T-SQL code to simulate these functions. But now there’s no need of doing so. Having available native function also helps performance as well readability.
SQL SERVER – SSMS 2012 Reset Keyboard Shortcuts to Default
SQL SERVER – Database Dynamic Caching by Automatic SQL Server Performance Acceleration
My second look at SafePeak’s new version (2.1) revealed to me few additional interesting features. For those of you who hadn’t read my previous reviews SafePeak and not familiar with it, here is a quick brief: SafePeak is in business of accelerating performance of SQL Server applications, as well as their scalability, without making code changes to the applications or to the databases. SafePeak performs database dynamic caching, by caching in memory result sets of queries and stored procedures while keeping all those cache correct and up to date. Cached queries are retrieved from the SafePeak RAM in microsecond speed and not send to the SQL Server. The application gets much faster results (100-500 micro seconds), the load on the SQL Server is reduced (less CPU and IO) and the application or the infrastructure gets better scalability.
SQL SERVER – Fundamentals of Columnstore Index
There are two kind of storage in database. Row Store and Column Store. Row store does exactly as the name suggests – stores rows of data on a page – and column store stores all the data in a column on the same page. These columns are much easier to search – instead of a query searching all the data in an entire row whether the data is relevant or not, column store queries need only to search much lesser number of the columns. This means major increases in search speed and hard drive use. Additionally, the column store indexes are heavily compressed, which translates to even greater memory and faster searches. I am sure this looks very exciting and it does not mean that you convert every single index from row store to columnstore index. One has to understand the proper places where to use row store or column store indexes. Let us understand in this article what is the difference in Columnstore type of index.
SQL SERVER – Three DMVs – sys.dm_server_memory_dumps – sys.dm_server_services – sys.dm_server_registry
In this blog post we will see three new DMVs which are introduced in Denali. The DMVs are very simple and there is not much to describe them. So here is the simple game. I will be asking a question back to you after seeing the result of the each of the DMV and you help me to complete this blog post.