In this blog post we will learn about Geography Data Type.
Answer simple quiz at the end of the blog post and –
Every day one winner from the United States will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 3.
Geography Data Type
New to SQL Server 2008 are the spatial data types, called Geography and Geometry. The Geography data type can store information for areas and points on the earth. It also provides a built-in function to calculate distance and overlaps with other locations. This data type stores and handles calculations based on round-earth (or ellipsoidal) data, which relates to coordinate systems such as GPS and longitude-latitude.
Databases stored positional data for years, like the sample data below where we see two dedicated fields to store longitude and latitude for each JProCo location. This is our first goal, we will do very soon after some more explanation.
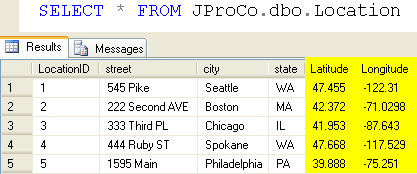
If you were to ask this table in a query what the longitude-latitude difference between Seattle and Boston is, it would have no idea. To the query, these are just arbitrary flat data values in a table. In order to turn each pair of numbers into a meaningful geographical point, we would have to extract this data into a custom application outside of SQL Server (e.g., into a C# application) and then run calculations using the customized app.
In other words, the true ellipsoidal nature of this geographic data wasn’t stored in the database prior to SQL Server 2008. The database couldn’t have differentiated our sample longitude-latitude data above from any other kind of information in the database. Now, thanks to SQL Server 2008, you no longer need a separate custom application, because both of these pieces of data can be stored in one Geography field. As well, the Geography type makes available all the built-in functionality, to perform calculations involving round-earth data, which would have been contained in a custom app.
Storing Latitude and Longitude
Prior to SQL Server 2008, float or decimal fields would be used to house latitude and longitude. Now you can store these, as well as other geospatial data, in one Geography field.
Let’s begin by looking at all the records in our Location table, as well as its design. We see typical location data – city, state, street – and the five JProCo office locations (Seattle, Spokane, Chicago, Boston, and Philadelphia). In this table, we will add fields for latitude and longitude, and then we’ll see how to combine those into one Geography field..


Let’s start by adding latitude and longitude fields and populate these fields using the values based on the code below:
ALTER TABLE Location ADD Latitude FLOAT NULL GO ALTER TABLE Location ADD Longitude FLOAT NULL GO UPDATE Location SET Latitude = 47.455, Longitude = -122.231 WHERE LocationID = 1; UPDATE Location SET Latitude = 42.372, Longitude = -71.0298 WHERE LocationID = 2; UPDATE Location SET Latitude = 41.953, Longitude = -87.643 WHERE LocationID = 3; UPDATE Location SET Latitude = 47.668, Longitude = -117.529 WHERE LocationID = 4; UPDATE Location SET Latitude = 39.888, Longitude = -75.251 WHERE LocationID = 5;
Creating Geography as a Field in a Table
We’re now going to add another field called GeoLoc (short for geographical location), which will use the new Geography data type. We have the latitude and longitude fields populated with values for each JProCo location. The Geography field GeoLoc has also been added to the table, but is not yet populated.


Populating a Geography Data Type
Based on the two data points, latitude and longitude, we can generate the geospatial locations for the GeoLoc field. Use the Point-static function called GEOGRAPHY to pass in the latitude and longitude values along with a style specifier value (4326 is the standard which is used the most).
UPDATE Location SET GetLoc = GEOGRAPHY::Point(Latitude , Longitude , 4326)

The style specifier we used to format our Geography value is also known as a spatial reference identifier or SRID and identifies which spatial reference system the coordinates belong to. The SRID 4326 represents WGS 84, which is the most commonly used systems and is used by many GPS systems.
Calculating Distance between two points on the earth
We have successfully combined latitude and longitude into the GeoLoc field. However, since the values in the GeoLoc column are a little cryptic to read by the human, we can create a variable and capture each city’s GeoLoc value into its respective variable.

STAsText( ) is one of the Spatial Type methods you can use with the Geography type. The STDistance( ) method calculates the shortest distance (in meters) between two Geography data points. To have STDistance( ) return the distance from Seattle to Boston in kilometers (KM), we have divided the returned value by 1000). Without this step, the result is just over 4 million meters (4,014,163 meters). Calculating the distance from Seattle to Boston, which is just over 4,014 KM.

Question 18
The STDistance function of the Geography Data type calculates the distance between two points in …
- Feet
- Meters
- Kilometers
- Miles
- Units
Do not forget to participate in special question over here: Pluralsight Giving Away Free Subscription to Quiz Participants
Rules:
Please leave your answer in the comment section below with correct option, explanation and your country of resident.
Every day one winner will be announced from the United States.
Every day one winner will be announced from India.
A valid answer must contain country of residence of answering.
Please check my facebook page for winners name and correct answer.
Winner from United States will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 3.
The contest is open till next blog post shows up at which is next day GTM+2.5.
Reference: Pinal Dave (https://blog.sqlauthority.com)





93 Comments. Leave new
2) is the answer as defined in this blog
2) Meters
Leo Pius
USA
Correct answer is option #3.
As stated clearly in the article above, STDistance( ) returns the distance in kilometers (KM)
Thanks.
Country – India
Correct option is #2.
2.Meters
New Delhi
India
The STDistance function of the Geography Data type calculates the distance between two points in Kilometers.Clearly, the best way to take advantage of the Geography Data Type is to use STDistance, as it returns meaningful set of numbers that can be understood by anyone..
Coon Rapids, MN
USA
Correct answer is #2 meters.
Uday Bhoopalam
USA
Hi,
It returns distance between 2 points in Meters.
Option 2 is correct.
Thanks
Sudhir Chawla
New Delhi, India
The STDistance function of the Geography Data type calculates the distance between two points in …
Feet
Meters
Kilometers
Miles
Units
Solution:
As per the definition and example the STDistance() method calculates the distance between two points in meters.
The answer is 2nd option.
Nagaraj Ejanthkar
USA
2. Meters
United States
Correct answer is No. 2.
The STDistance( ) method calculates the shortest distance (in meters) between two Geography data points.
Rene Castro
El Salvador
option 2 is the right answer
The STDistance function of the Geography Data type calculates the distance between two points in “Meters”
The return measurement depends upon the Spatial Reference Identifiers (SRIDs) of our geography data type. The default is 4326 which is in meters. There’ a table in the DB we can check-
Select * from sys.spatial_reference_systems
Regards
Santosh.S
Bangalore, India
Meters
ADITI S
BOSTON, USA
Quick Question… u mentioned geography and Geometry . where is the geometry part??
oops ..my bad it doen’t say geometry
The STDistance function of the Geography Data type calculates the distance between two points in …
Answer is:
3. Kilometers
India,Banglore
Answer is
2. Meters
Option 2 is the Right answer
Manoj Sahoo
India
Question 18
Ans : Meters
Chennai, INDIA
Correct answer is option #2.
Meters
Thanks,
Dhruval Shah – India
The correct answer is 2 – meters. Thanks for very helpful lesson!
I am from USA
answer is second – Meters
India
Correct answer is # 2.
The STDistance( ) method calculates the shortest distance (in meters) between two Geography data points.
Gopalakrishnan Arthanarisamy
Unisys, Bangalore, India