When I pen down any article I always keep my readers in my mind. With every topic of SQL server I cover, I try to bring readers closer to this technology. So, whenever I receive follow up questions from my readers I am exhilarated! Sometime back I had covered a topic – SQL SERVER – Create Multiple Filegroup For Single Database, for which I received a number of follow up questions. In this post I would like to discuss on a question from one of the readers Joginder “Jogi” Padiyala.
“How can I find which object belongs to which filegroup. Is there any way to know this?”
Well, finding out which object belongs to which table is very simple.
Let us first create a database having multiple filegroups.
/* Create Database
Please note that there are two Filegroups for newly created datbase.
MDF - Primary and LDF on Secondary */
CREATE DATABASE [FGTest] ON PRIMARY
( NAME = N'FGTest',
FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\FGTest.mdf' ,
SIZE = 3072KB , FILEGROWTH = 1024KB ),
FILEGROUP [Secondary]
( NAME = N'FGTest_2',
FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\FGTest_2.ndf' ,
SIZE = 3072KB , FILEGROWTH = 1024KB )
LOG ON
( NAME = N'FGTest_log',
FILENAME = N'C:\Program Files\Microsoft SQL Server\MSSQL10.MSSQLSERVER\MSSQL\DATA\FGTest_log.ldf' ,
SIZE = 1024KB , FILEGROWTH = 10%)
GO
Now create a table on primary filegroup.
/* Create New table on Primary Filgroup */
USE [FGTest]
GO
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TestTable](
[ID] [int] NOT NULL,
[Col1] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
[Col2] [varchar](50) NOT NULL,
CONSTRAINT [PK_TestTable] PRIMARY KEY CLUSTERED
(
[ID] ASC
)
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Next, create non-clustered index on secondary filegroup.
/* Create Non Clustered Index on Secondary FileGroup */
CREATE NONCLUSTERED INDEX [IX_TestTable_Second] ON [dbo].[TestTable]
(
[Col1] ASC
) ON [Secondary]
GO
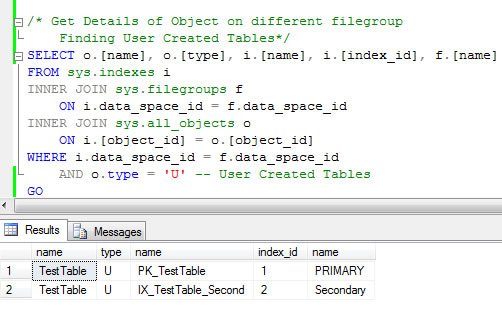
After that, we will run the following T-SQL and determine where all the objects are located on filegroup. We have already created a non-clustered index on our table. Now, non-clustered table creates its own table, which consists of pointers to clustered index. For the same reason, we will search with additional condition of object type, which will list only user created tables. Non- clustered table should be part of user created table group.
/* Get Details of Object on different filegroup
Finding User Created Tables*/
SELECT o.[name], o.[type], i.[name], i.[index_id], f.[name]
FROM sys.indexes i
INNER JOIN sys.filegroups f
ON i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
INNER JOIN sys.all_objects o
ON i.[object_id] = o.[object_id]
WHERE i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
AND o.type = 'U' -- User Created Tables
GO
Let us observe the same query again with different WHERE condition. Here we are retrieving everything that is on secondary filegroup. It is very easy to identify filegroup name and data by just selecting everything from system table sys.filegroups.
/* Get Detail about Filegroups */
SELECT *
FROM sys.filegroups
GO

In our case, secondary filegroup has data_space_id as 2. Now, we will run the following query and figure out which objects are located on filegroup 2.
/* Get Details of Object on different filegroup
Finding Objects on Specific Filegroup*/
SELECT o.[name], o.[type], i.[name], i.[index_id], f.[name]
FROM sys.indexes i
INNER JOIN sys.filegroups f
ON i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
INNER JOIN sys.all_objects o
ON i.[object_id] = o.[object_id]
WHERE i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
AND i.data_space_id = 2 -- Filegroup
GO

I hope this answers Jogi’s question and is helpful for those who were curious to know the answer to this topic.
Reference : Pinal Dave (https://blog.sqlauthority.com)






44 Comments. Leave new
Very Interesting.
Thanks.
Never got a chance to work with Multi file groups yet.
~ IM.
Hello Pinal,
When do we create a File Group?
In our prod environment we have a db with 3 datafiles and 1 log file,
All the 3 dbs have the same size 16 gb and the log file is 5 gb.
They are all on the PRIMARY file group.
All the 4 files are on four different drives.
I am just wondering whether creating File Groups here will help?
Thanks
Biju
Hi,
Thank you very much for nice articles.
regards
patar
Hello Sir,
It’s very nice article and i try to find about the
how i can get file groups in primary key it is very use ful
to create script for primary key.
Thnaks,
Kuldip Bhatt
What about statistics? What I mean is before SQL 2008/2005 we had groupid for sysindexes, which also contained stats info.
Now there’s sys.indexes and sys.stats. sys.indexes has data_space_id, sys.stats does not. How is this handled in SQL 2008 then?
Thanks for your help…
Thanks for spreading knowledge, it is a nice article.
This is a very handy article but I see one flaw. It presumes that your object has an index. How would this be done if the object doesn’t have an index?
Per MSDN,
Sys.indexes “Contains a row per index or heap of a tabular object, such as a table, view, or table-valued function.” So it should be good.
Can we move udf stored procs and functions from PRIMARY to different filegroup?
thanks for the articles
If you have partitioned tables and you use this queries you cant see the that some partitions reside at some filegroups. You think that there’s no objects in a filegroup but there are lots of partitions.
For instance: I have 4 filegroups and none table created in one specific filegroup but in some partition schemes that use the four filegroups. When you query sys.indexes and sys.filegroups none objects are displayed.
Pinal,
I am working on file group audit and saw the same script you are using at mssqltips.com )
But I also want to find the view, procedures and functions on the filegroup. I could not find a way to do that. I will appreciate if you can help me with that.
Your community spirit is unparalleled. I like to come to your blog when I have problem at my work to look for solution and many a time I have found one.
Hi Pinal,
Writtten this SP to find the large tables in the filegroup. Handy when you need to move large tables to other filegroups.
CREATE PROC sp_show_huge_tables
(
@top int = NULL,
@include_system_tables bit = 0
)
AS
/*************************************************************************************************
Purpose: To list the size of all tables in the database in descending order (that is biggere tables first).
Output can be restricted to top n tables. That is you can pass the value 3 to @top parameter to
see the top 3 biggest tables in your database. Optionally, you can use @include_system_tables
parameter, to include systemt tables in the output.
NOTE: Always create this procedure in the master database and call it from the required databases,
as if the stored procedure is created in that database (That is, don’t prefix the stored procedure
with the database name).
Written by: John Saldanha
Tested on: SQL Server 10.0
Date created: October – 4 -2010 2:00:00 PM IST
Date modified: October – 4 -2010 2:00:00 PM IST
Examples:
To list all the user tables in the database along with their sizes:
EXEC sp_show_huge_tables
To see the top three biggest tables in your database:
EXEC sp_show_huge_tables 3
To list all the user AND system tables in the database along with their sizes:
EXEC sp_show_huge_tables @include_system_tables = 1
To see the top three biggest user or system tables in your database:
EXEC sp_show_huge_tables 3, 1
*************************************************************************************************/
BEGIN
IF @top > 0
SET ROWCOUNT @top
SELECT [Table Name], (SELECT rows FROM sysindexes s WHERE s.indid < 2 AND s.id = OBJECT_ID(a.[Table Name])) AS [Row count], [Total space used (MB)], FileGroup FROM
(
SELECT QUOTENAME(USER_NAME(o.uid)) + '.' + QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(i.id)) AS [Table Name],
CONVERT(numeric(15,2),(((CONVERT(numeric(15,2),SUM(i.reserved)) * (SELECT low FROM master.dbo.spt_values (NOLOCK) WHERE number = 1 AND type = 'E')) / 1024.)/1024.)) AS [Total space used (MB)], f.name As FileGroup
FROM sys.sysindexes i (NOLOCK)
INNER JOIN
sysobjects o (NOLOCK)
ON
i.id = o.id AND
((@include_system_tables = 1 AND o.type IN ('U', 'S')) OR o.type = 'U') AND
((@include_system_tables = 1)OR (OBJECTPROPERTY(i.id, 'IsMSShipped') = 0))
INNER JOIN sys.filegroups f
ON i.groupid = f.data_space_id
WHERE indid IN (0, 1, 255)
AND i.groupid = f.data_space_id
GROUP BY QUOTENAME(USER_NAME(o.uid)) + '.' + QUOTENAME(OBJECT_NAME(i.id)), f.name
) as a
ORDER BY [Total space used (MB)] DESC
SET ROWCOUNT 0
END
GO
Hi Pinal,
Great post.
It would be nice to have the size of the table/index as well along with the file group in which it is stored. The administrator can then concentrate only on tables/indexes with large size.
Hi…
I hope everything will go smoothly. and wanted to know if anyone knows how I can define the GOTO instruction and that taken as a parameter eg @ GoTo Label
Escuchar
Leer fonéticamente
Diccionario – Ver diccionario detallado
I hope everything will go smoothly. and wanted to know if anyone knows how I can define the GOTO instruction and that taken as a parameter eg: GoTo @Label
Thks
Thanks for the post!
I needed to relate tables to files so I added sys.master_files:
Select Distinct
O.name As TableName
,I.name As IndexName
,I.type_desc As IndexType
,I.index_id As IndexID
,FG.name As FileGroupName
,F.name As FileLogicalName
,F.physical_name As FilePhysicalName
From
sys.indexes As I
Inner Join
sys.filegroups As FG
On I.data_space_id = FG.data_space_id
Inner Join
sys.master_files As F
On FG.data_space_id = F.data_space_id
And F.database_id = DB_ID()
Inner Join
sys.all_objects As O
On I.[object_id] = O.[object_id]
Where
I.data_space_id = FG.data_space_id
And O.[type] = ‘U’
Order By
TableName
,IndexID
Go
Hi Pinal,
What is the main impact on performance if a table have 1000k Rows and more than 100 indexes on it.
How much max indexes are sufficient in a large table.
I know if the size of the table increases it decreases the performance as well. However we have a high performance database server.
Thanks
Shyam
Hi Pinal,
In both your queries given above, you have the following conditions:
1. ON i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
2. WHERE i.data_space_id = f.data_space_id
However, the Where clause looks duplicated since the views have already been joined. Please let me know your thoughts on this.
Cheers,
Shankar
Can we group any other SQL objects other than table and index, under different file groups ?
Hi Pinal. I have a partitioned table with 4 filegroups. Each filegroup has two data files. SQL server is only writing to one data file of each files group. The second datafile for every filegroup is empty. I load 30 million rows a day. Before I log a call to Microsoft, do you have any ideas
Many Thanks
Mohamed