Earlier in this blog, I have written a number of posts by using PowerShell. The more you play around with this scripting language more are the hidden gems that come out. Personally for me, everyday is like a new learning that needs to be discovered working with SQL Server and PowerShell. One of the posts that I would like to recollect is: PowerShell – Querying SQL Server From Command Line
In the post mentioned above, I have mentioned one of the ways to query SQL Server from command line. This blog post is almost on similar lines in some way. But in this blog post, I will want to show the PowerShell commandlet for querying SQL Server.
Let me introduce you to Read-SQLTableData. When I saw this command, I went to my SQL Server box to check how this works. It was amazing to see the output from the PowerShell window. From SQL Server Management Studio, I went to a database, expanded Tables and selected a table with right click and “Start PowerShell”. In this example, I have taken the AdventureWorks, dbl.DatabaseLog table. Once on command prompt, fire the powershell commandlet as shown below:
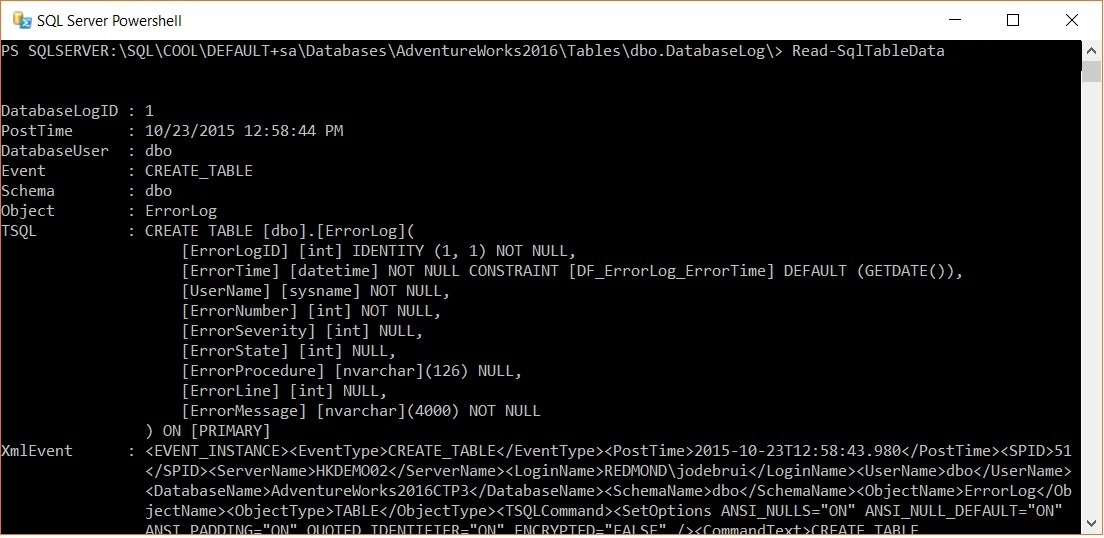
This gets this simple from a query pattern point of view. It will display the complete table data on the console. From this is a console, we can always take the output to a .txt file if required.
One of the addendum to this is the ability to add few interesting parameters to the same query.
Read-SQLTableData -top 2 -OutputAs DataTable -ColumnName Event,Schema,Object,PostTime
Here in the above query, I have gone ahead to take the top 2 rows and have explicitly called out the column names of interest. The typical output of this would look like:
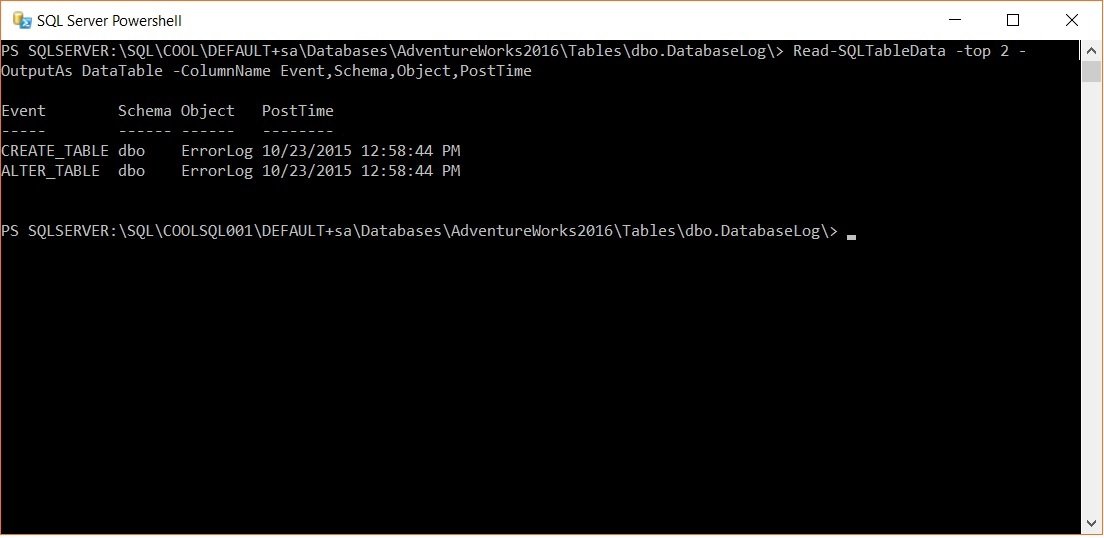
Interesting, isn’t it? I am sure once you start to play with PowerShell and the SQL commandlets, you will find interesting use cases of using the same. Feel free to let me know how you used this in your environments.
Reference: Pinal Dave (https://blog.sqlauthority.com)





1 Comment. Leave new
Hi Pinal,
I’ve used PowerShell 2.0/3.0 quite a bit in my current position. I’m the primary software engineer that writes up all the PS scripts we used in our Tech Ops department.
Couple of things we’ve done in PowerShell:
1. Backup / Update / Restore Databases and Cubes.
2. Install and Remove multiple SSIS packages on Integration Services.
3. Check what remote servers users are still logged on and log them off.
4. Migrate and update configuration files between different servers using test-path, get-childitem, rename-item, get-content, $_.replace, set-content, etc.
5. Extract data from SQL Server into an Excel file, format and encrypt the file, and send out an email with the attachment. Send failure notification if outbound email fails.
6. Pull data from different servers and insert it into a single database with the option to multithread on the local machine or the remote servers. Cut down retrieval time from ~2 days to 20-25 minutes.
7. Retrieving available disk space from all servers into a single report.
PowerShell is pretty awesome. I’m glad it will be available on Linux.
Best,
Jason