 Answer simple quiz at the end of the blog post and –
Answer simple quiz at the end of the blog post and –
Every day one winner from India will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 4.
Every day one winner from United States will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 4.
SQL Server Error Messages
By now, most readers have likely learned that it is better to deal with problems early on while they are small. SQL Server detects and helps you identify most errors before you are even allowed to run the code. For example, if you try to run a query against a table which does not exist, SQL Server informs you via IntelliSense while you’re coding the query or via an error message when you attempt to run the query. You also will get an error message if you try to insert a null value into a non-nullable field. This section will cover how SQL Server raises error messages.
Errors in SQL Statements
SQL Server will raise errors when the code you have written cannot or should not execute. For example, a table should not be created if one with the same name already exists. Also, you can’t run a stored procedure if the name you are calling does not exist. Attempting to run such code will cause SQL to raise an error.
SQL Server raises an error whenever a statement cannot, or should not, complete its execution. For example, we know there is already an Employee table in the JProCo database. In the figure below we see code to create another Employee table. If we attempt to run the code below, should SQL Server permit our longstanding Employee table to be overwritten?

Having a new, empty Employee table overwrite the one we are using would not be a good idea. In the figure below we see SQL Server prevented the accidental loss of the valuable data in the existing Employee table. When we run this, SQL Server alerts us that our code cannot be run and displays the reason in an error message. Notice that this is error message 2714. Error severity levels range from a low of 0 to a maximum of 25, and the error severity level here is 16. We will discuss error severity more in tomorrows post.

A perfectly written table creation statement sometimes will work and under other conditions it may error out. With the code below the SometimesBad stored procedure will sometimes throw an error message. If SQL finds the TempStaff table, then it will attempt to run the table creation statement. Imagine the TempStaff table didn’t exist. In that case, nothing would happen. The IF EXISTS condition would be false so the CREATE TABLE statement would not be attempted.
CREATE PROC SometimesBad
AS
BEGIN
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE [name] = 'TempStaff')
CREATE TABLE TempStaff (TStaffID INT NOT NULL, TStaffName VARCHAR(100) NULL)
END
We know one way to generate an error is to try creating a table which already exists. Another way is to try dropping a table which doesn’t exist. If you run the SometimesBad stored procedure, it will only throw an error if the TempStaff table already exists. For testing purposes, we want a stored procedure like SometimesBad to always throw an error message. Our next step will be to add an ELSE statement which says that we want to drop the table if it is not found.
Look closely at this code and recognize that it will always throw an error. If the TempStaff table exists, then trying to execute a statement to create this table generates an error. And if the TempStaff table doesn’t exist, then executing a statement which attempts to drop this table will similarly generate an error.
CREATE PROC AlwaysBad
AS
BEGIN
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM sys.tables WHERE [name] = 'TempStaff')
CREATE TABLE TempStaff (TStaffID INT NOT NULL, TStaffName VARCHAR(100) NULL)
ELSE
DROP TABLE TempStaff
END
If you were to create and run the AlwaysBad sproc, you would see that attempting to execute it will always result in an error message. During the sproc execution, SQL tried to create the TempStaff table which already existed. If the table is not present, then the same stored procedure would still throw an error. Message 3701 indicates that you can’t drop the table because it does not exist.
EXEC AlwaysBad
Msg 3701, Level 11, State 5, Procedure AlwaysBad, Line 7
Cannot drop the table ‘TempStaff’, because it does not exist or you do not have permission.
RAISERROR
Again, we know that SQL Server will raise an error whenever a statement cannot, or should not, complete its execution. It’s also possible to define your own conditions where SQL Server does not encounter an error but nonetheless doesn’t run due to a situation which goes against company policy. For example, updating an employee’s payrate to below minimum wage is not a SQL error. However, in such a situation you would prefer that SQL Server generate an error message rather than allowing that code to execute.
Suppose you have a stored procedure named UpdateOneEmployee which changes one employee record at a time. The logic of this stored procedure will allow you to potentially update two employees with the same info. Since it is against company policy to update more than one employee record a time, it’s extremely unlikely that anyone would ever attempt to update multiple records at once. However, because SQL Server has no restriction against updating or many records in one transaction, you want to add a layer of protection to help enforce company policy. This is a case where you don’t want SQL Server to allow this update, even though SQL Server doesn’t define it as an error. To accomplish the needful, you can raise your own error message based on conditions which you define.
ALTER PROC SetEmployeeStatus @EmpID INT, @Status VARCHAR(20)
AS
BEGIN
UPDATE Employee SET [Status] = @Status
WHERE EmpID = @EmpID
END
We can confirm the status change by querying the Employee table. Passing the values 1 and ‘On Leave’ into SetEmployeeStatus changes the Status field for Employee 1 to ‘On Leave.’ This changes the value of EmpID 1. Let’s execute this statement for an employee which doesn’t exist. Notice that our result is not actually an error. The statement runs alright, but no rows are affected because no records in JProCo’s Employee table meet the criteria.

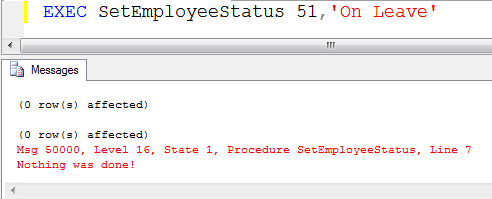
This is not a SQL Server error since it’s OK to update zero records. But what if the 51 was a typo? What if the intent was to update the status for Employee 11 or Employee 21? In that case, it would be helpful to program your code to alert you if you accidentally attempted to run a statement for a non-existent EmpID. Let’s alter the stored procedure by adding two more statements. If we see that no rows are affected then we will raise a level 16 error that alerts us, “Nothing was done!”

With the sproc updated, let’s run our prior EXEC statements for EmpID 1 and EmpID 51. EmpID 1 runs the same as it did previously. Here you can see that calling on the stored procedure and passing in 51 for the EmpID returns our user-defined error message. The severity is level 16 and the message says “Nothing was done!”
Note: If you want to setup the sample JProCo database on your system you can watch this video. For this post you will want to run the SQLProgrammingChapter8.1Setup.sql script from Volume 4.
Question 27
When does SQL Server always raise an error message? (Choose two)
- When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
- When multiple records are updated in one table
- When you issue a RAISERROR message
Rules:
Please leave your answer in comment section below with correct option, explanation and your country of resident.
Every day one winner will be announced from United States.
Every day one winner will be announced from India.
A valid answer must contain country of residence of answerer.
Please check my facebook page for winners name and correct answer.
Every day one winner from India will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 4.
Every day one winner from United States will get Joes 2 Pros Volume 4.
The contest is open till next blog post shows up at which is next day GTM+2.5.
Reference: Pinal Dave (https://blog.sqlauthority.com)






54 Comments. Leave new
Correct answers are 1 and 3: SQL Server always raise an error message when a statement in SQL Server cannot run or when someone issues a RAISERROR message.
Rene Castro
El Salvador
When a statement cannot run – SQL Server will tell you why it cannot run that particular statement, either there is some kind of violation such as security, constraint/rule or the syntax is wrong or similar
When you issue a raiseerror message – the raiseerror message is specifically intended for user defined error situations such as the one above, updating multiple records. When a raiserror is encountered sql does not worry about underlying cause just raises the error.
———————-
From USA
Very nice write-up and congratulations on the book! 1 and 3 by the way. *smile*
Answers are 1 and 3
SQL will raise an error “When a statement in SQL Server cannot run” but you can also write your own messages to alert when certain things happen that you don’t want. This is where #3 (When you issue a RAISERROR message) comes in.
USA
Hi,
options 1 and 3 fit in. Options 2 is incorrect because updating/deleting 0 to n rows will depend entirely upon number of rows returned by the WHERE clause. Therefore, multiple update might be a logical error.
SQL Server throws an error when:
1. it encounters incorrect syntax or such statements which it cannot execute (Option 1)
2. We code an error raising statement (Option 3)
Ramakrishnan RS
Mysore, India
1)When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3)When you issue a RAISERROR message
These two are correct.
Arjun,
INDIA
1) and 3)
Error is thrown when a statement cannot execute when the user uses the RAISERROR statement
Leo Pius
USA
Answer is Options [1] and [3] ..
Answers option 1 and option 3
1)When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3)When you issue a RAISERROR message
RIYAS.V.K
INDIA
Ans :1 and 3
1.When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3.When you issue a RAISERROR message
When a sql statement can not run it will through an error message due to some
violation like security, constraint/rule or the syntax is wrong or for an object which dose not exits or similar.So option 1 is correct.
if we manually wants to raise an error which is not sql server error like we don’t
want to drop a table for that we write a ddl trigger there we roll back the drop action an raise an error.sql server always throw that error. so option 3 is also correct.
But update multiple record in a table is not an sql server error it allows user to update multiple record. In that case sql server does not through an error except we does not raise it manually. so option 2 is incorrect.
Partha,
India
SQL Server always raise an error message on following 2 occasions
1. When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3. When you issue a RAISERROR message
When a statement like dropping a table which does not exists or creating a table which is already present, then SQL server would raise an error message.
Also when we explicitly specify RAISERROR message then the same is taken care by SQL server if any error occurs related to the same.
Kedar – India
1. When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3. When you issue a RAISERROR message
These are the correct options. SQL Server raises error where some erroneous condition occurs or user raises error on particular special event.
Error occurs when :
a) Database object/Column not Exists
b) Constraints Violation (Primary key, foreign key, not null, check etc.)
c) Syntax errors
d) Column not added in “group by ” clause but used in select list with aggregate functions.
e)User don’t have rights to perform specific operation. etc.
Thanks,
Shirish,
India
Answer is 1 and 3. SQL throws error in these two scenarios and regarding option 2 it’s about multiple record update which is allowed for a table in SQL.
Sathya, chennai, India
1)When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3)When you issue a RAISERROR message
These two are correct.
lalit,
INDIA
Options 1 & 3 are the correct Answers for this Question.
Thanks,
Narendra(India)
Correct answers are 1 & 3.
New Delhi
India
Hi,
Correct option is
1 and 3
I am from India.
Correct answer would be option # 1 & 3.
if you have any mistake in statement than obviously, compiler would throw the error.
and RAISEERROR intend to use pop up the error.
Ritesh (India)
Correct Answers are # 1 & 3.
1. When a statement in SQL Server cannot run.
3. When you issue a RAISERROR message.
SQL Server always raise an error message when a statement in SQL Server cannot run or when someone issues a RAISERROR message.
Gopalakrishnan Arthanarisamy
Unisys, Bangalore, India.
the correct answer is Options 1 & 3 i.e.
1)When a statement in SQL Server cannot run
3)When you issue a RAISERROR message
India